Essentials of Spark Architecture
Apache Spark is originally built on RDD abstraction and it is constructed in a well defined layered architecture. DataFrames and Datasets are used in modern spark applications.
In its core, Spark has three main components.
- Driver Program
- Cluster Manager
- Spark Executors
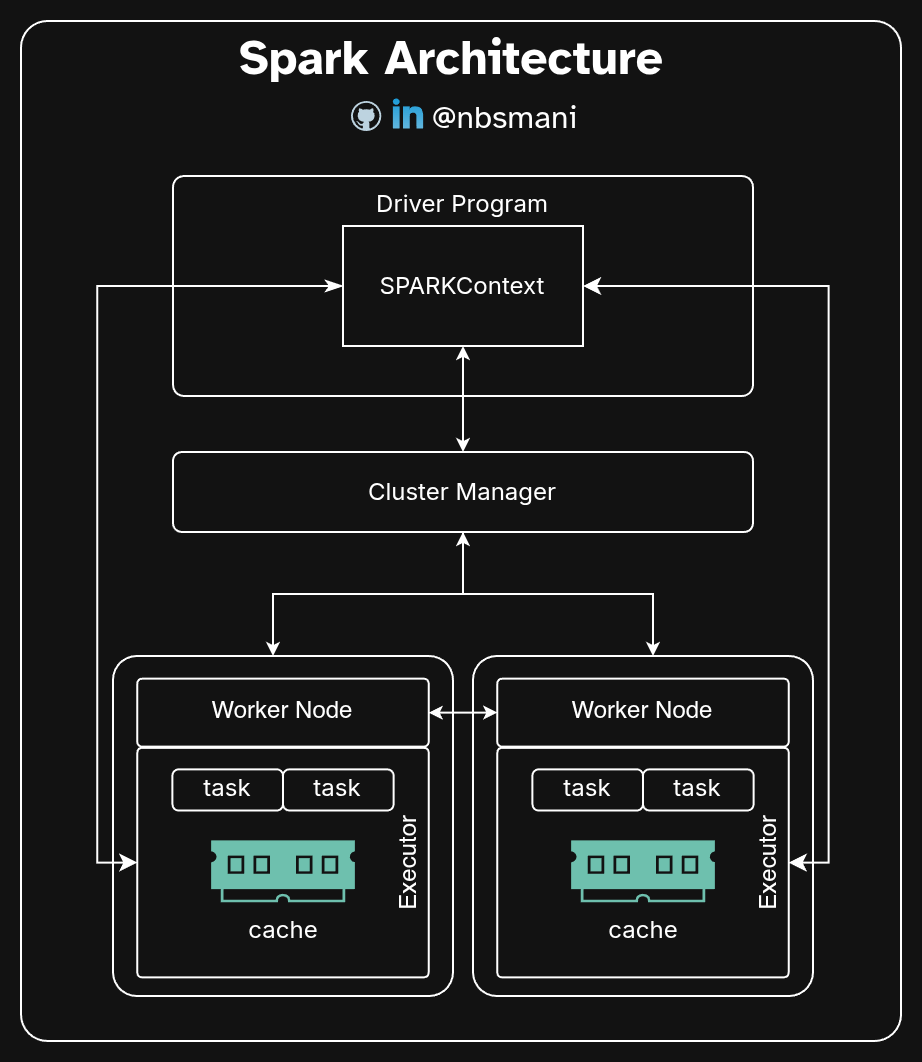
Driver Program:
Any script that uses spark to process big (and not so big) data is a spark application. The Driver program is the entry point of the application and it is where the main script is hosted.
The driver program reads the script and creates a logical plan of operations Directed Acyclic Graph. In spark, there are two types of operations. Transformations and actions. The DAG is comprised of these transformations and actions. The smallest sub unit of any operation is a task and a set of tasks are grouped in a stage. Spark DAG is built according to the logic of the user’s application. The logical DAG is broken down into stages and TaskScheduler serializes and assigns individual tasks. The Driver program stores the metadata of the tasks shared with the executors and the results are collected back once the tasks are completed. The taks lineage is readily available in the driver so that it can quickly rebuild a lost partition in case a failure. The process of building serialized stages is called DAG scheduling. The scheduled DAG stages are then transferred to Task Scheduler. TaskScheduler assigns tasks to executors. Actual execution happens only when an action is required, this is the so called ‘Lazy Evaluation’.
SparkSession and SparkContext
SparkSession
SparkSession is the latest implementation in Spark v>2.x.x. The Driver program creates SparkSession which is the entry point of a program. In SparkSession, along with SparkContext, SQL, Streaming, ML and Graph context are available and unified into one engine under the same SparkSession offering superior flexibility. SparkContext is now available as backward compatible to access low level RDD features. Since the higher level APIs are accessible with SparkSession, Apache recommends to initialize with SparkSession.
SparkContext
SparkContext is created by the driver program and this was formerly the entry point until spark 2.x.x. SparkContext connects to the cluster manager and acquires the required resources for the distributed computation. It then sends the serialized DAG stages to the executor nodes and keeps track of the execution via regular heart beat messages.
Cluster manager :
The computing resources are managed by the cluster manager. There are three different types of cluster management in Spark. Namely, Spark standalone, Kubernetes and YARN. Often the resource manager resides in master node but this depends on the deployment mode of the application. In local deployment mode, The driver and executor nodes are hosted in a single thread and spark manages the threads itself and no cluster manager is involved in this case.
The resource manager receives requests from the task scheduler and launches executor processes on the worker nodes. The executor process(es) are launched in pods (kubernetes), containers /raw processes (spark standalone) depending on the configuration of the deployment. It then pings back the availability of the worker nodes and a connection is established between the spark driver program and the worker nodes.
Executors
The executor manages the task execution and manages the memory, it communicates with the driver program to report the status of the assigned tasks and return the computed results. The executors are also involved in shuffle operations and act as a server for other executors to access the local data of the executor.